Machinery onboard ships require regular care and
maintenance so that their working life and efficiency can be increased, and the
cost of operation, which includes unnecessary breakdowns and spares, can be
reduced. For different types of machinery and systems, various measuring tools,
instruments and gauges are used on a ship.
Measuring instruments and gauges are used to measure various
parameters such as clearance, diameter, depth, ovality, trueness, etc. These
are critical engineering parameters, which describe the condition of the
working machinery.
Below, we have compiled a list of mechanical measuring
instruments and mechanical gauges which are extensively used on the ship for
the recording of different parameters.
Popular mechanical gauges and
tools used on ships:
There are many instruments, tools and gauges which are used
on a daily basis onboard ship for measurement, fault finding, wear down etc.

Popular mechanical gauges and
tools used on ships are:
Ruler and scales
They are used to measure lengths and other geometrical parameters.
This tool is one of the most famous measuring instruments in mechanical
engineering. They can be a single steel plate or a flexible tape type tool.
They are usually available in the measuring scale of inch or cm.
They are used for quick measurement of parts and always kept
with other measuring gauge or tools in the workshop for handy access. The ruler
and scales are not used where precise measurement is required. It is made from
stainless steel which is durable and will not rust or corrode.
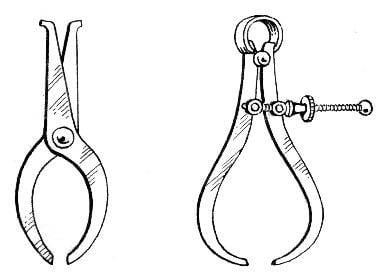
Calipers
They are usually of two types- inside and outside calliper.
They are used to measure internal and external size (e.g. diameter) of an
object. It requires an external scale to compare the measured value. This tool
is used on those surface where a straight ruler scale cannot be used. After
measuring the body/ part, the opening of the calliper mouth is kept against the
ruler to measure the length or diameter.
Some callipers are integrated with a measuring scale; hence
there is no need of other measuring instruments to check the measured length.
Other types are odd leg and divider calliper.
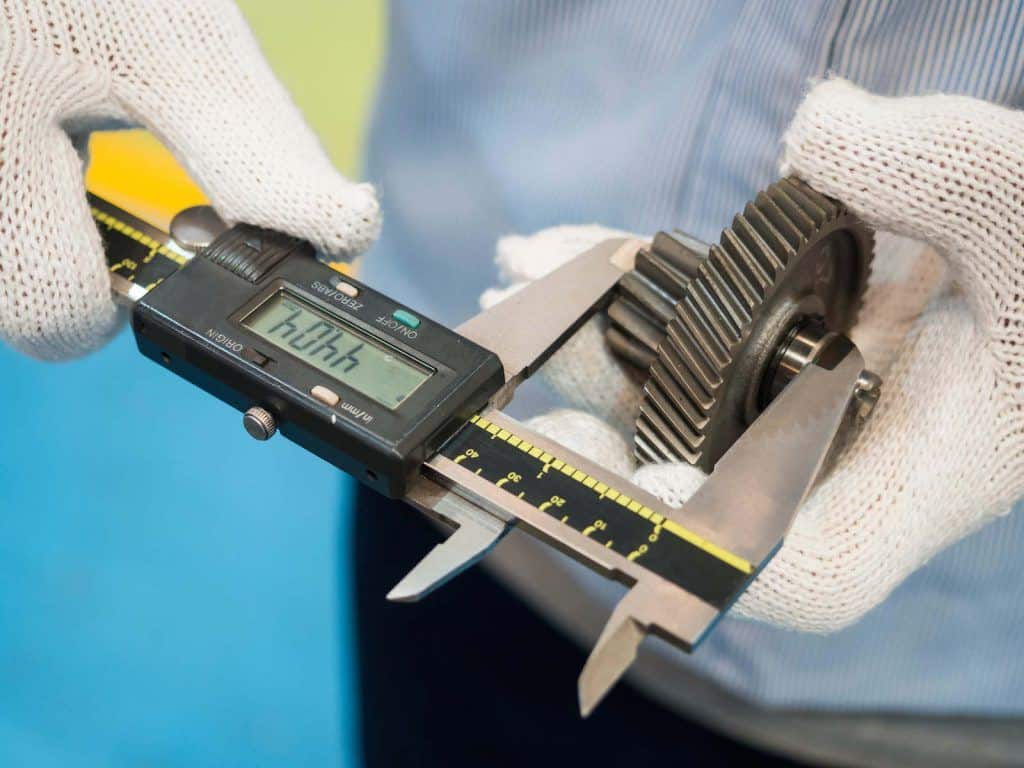
Vernier Caliper
It is counted in the list of quality measuring instruments,
which are used to measure small parameters with high accuracy. It has got two
different jaws to measure outside and inside dimensions of an object. It can be
a scale, dial or digital type Vernier calliper. Vernier calliper is one of the
most used mechanical measuring tools onboard ship.
Least count of the vernier calliper is the difference
between the values of main scale division and one vernier scale division.
Least Count= Value of one main scale division – Value of one
vernier scale division.
= 1 mm – 9/10 mm = 1 mm – 0.9 mm = 0.1 mm or 0.01 cm

Micrometer
It is an excellent precision tool which is used to measure
small parameters and is much more accurate than the vernier calliper. The
micrometre size can vary from small to large. The large micrometre calliper is
used to measure large outside diameter or distance. E.g. Large micrometre is
used as a special mechanical measuring tool for main engine to record the outer
diameter of the piston rod.
They are available in two types- Inside micrometre (to
measure inside diameter) and Outside micrometre (for measuring outside
diameter).
The Least count of the micrometre is 0.01 mm or 0.001cm.

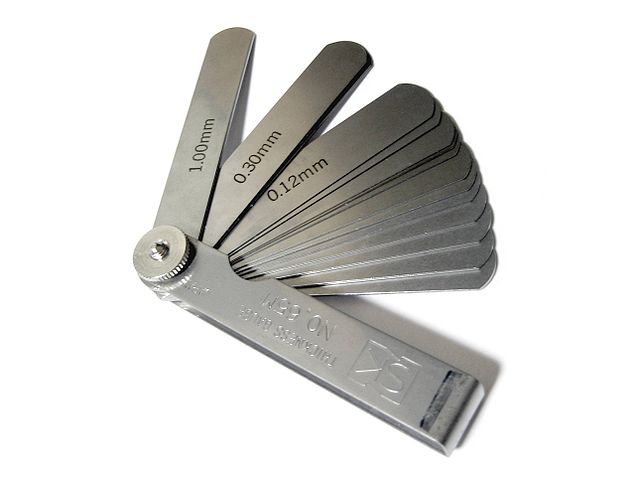
Feeler gauge
Feelers gauges are a bunch of fine thickened steel strips of
different thickness bundled together. The thickness of each strip is marked on
the surface of the strip. The feeler gauge is used to measure the clearance or
gap width between surface and bearings.
E.g. The feeler gauge is widely used to measure piston ring
clearance, engine bearing cleaner, tappet clearance etc.

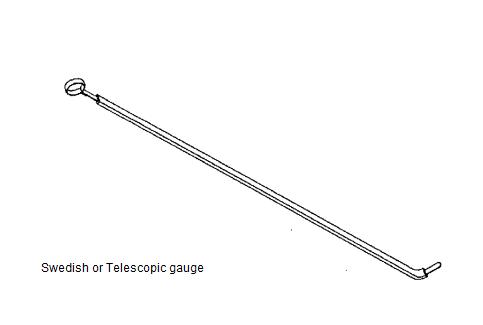
Telescopic Feeler Gauge
Similar to the functionality of feeler gauge, this type of
gauge is also known as tongue gauge, and it consists of long feeler gauge
inside a cover with tongue or curved edge.
The long feeler strips protrude out of the cover like a
telescope so that it can be inserted into remote places where feeler gauge
access is not possible. E.g. It is used to measure the bearing clearance of the
top shell.
It is essential that after the use of the telescope gauge,
the strip should be cleaned and retracted back to its housing, else it may
damage the feeler strip.
Poker Gauge
Poker gauge is one unique tool among different types of
measuring instruments is available in mechanical or digital form on
ships. It is only used for one purpose; To measure propeller stern shaft
clearance, also known as propeller wear down. It is a type of depth measuring
instrument, whose reading indicates the wear down of the stern shaft.
A special access point or plate is provided which can be
either open, bolted, secured or welded, depending upon the ship design. The
Poker gauge is inserted to in this access point to measure the propeller drop.
The poker gauge is a special instrument which is kept with the chief engineer,
and the reading is usually taken every dry
dock.
The design of the poker gauge may vary as each vessel has customized
poker gauge made available during the handing over from the shipyard. While
taking the reading the shaft to be turned, so that propeller boss matches with
the marking of the shaft.
Bridge Gauge
As the name suggests, Bridge gauge looks like bridge
carrying the measuring instrument at the centre of the bridge. They are used to
measure the amount of wear of Main engine bearing. Typically the upper bearing
keep is removed, and clearance is measured for the journal. A feeler gauge or
depth gauge can be used to complete the process.
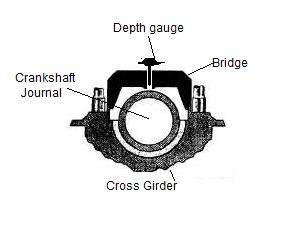
depth gauge can be used to complete the process.
Liner Measurement Tool
A liner measurement tool is a special tool for marine
engines which comes in a set of the straight rod of different marked length,
which can be assembled together to make the measuring tool of the required
length. It is used to measure the wear down or increase the diameter of the
engine liner.
It is considered as special tools when compared to other
types of measuring tools and kept separately with other engine special tools
under chief engineer or 2nd engineer supervision.

A feeler gauge or American Wire Gauge
American wire gauge or AWG is a standard tool which is
circular and has various slots of different diameter in its circumference. It
is used to measure the cross section of an electric cable or wire. This tool is
usually kept in the electrical workshop of the ship, and electrical officer
uses it for measuring wire thickness.

Bore Gauge
A tool to accurately measure the diameter of any hole is known
as bore gauge, It can be a scale, dial or digital type instrument. The most
common type which is used on the ship is dial type bore gauge, which comes with
a dial gauge which is attached to the shaft and replacement rods, also known as
measuring sleds, of different size to measure different hole dimensions.
It is usually calibrated in 0.001 inch (0.0025 cm) or 0.0001 inch (0.00025 cm).

Depth Gauge
A depth gauge is used to measure the depth of a slot, hole
or any other surface of an object. It can be of scale, dial or digital type.
The depth gauge can be a micrometre style type, a dial indicator type, or
modified Vernier type tool, which means the measuring base is fitted on the
reading scale of a micrometre, dial indicator or the Vernier scale.
Angle Plate or Tool
As the name suggests, this is a tool comprising of two flat
plates which are at a right angle to each other, and it is used to measure the
exact right angle of an object or two objects joined together. This tool is
usually kept in workshop away from any tools or chemical which may roughen the
surface of the angle plate.

NtescoFpoebu Joseph Robinson link
ردحذفswiseartesa